Houstonia L. (Rubiaceae)
Houstonia had been represented by nine taxa in North Carolina, until recent work found persistent populations of H. micrantha (native to the Deep South) and H. procumbens (State SR-P, S1 G5; apparently spreading north from South Carolina; neither yet keyed below). Both would fall under lead 1. below. Both exhibit white corollas. Houstonia micrantha is an annual most similar to H. pusilla, except for the white (and smaller) corollas. Houstonia procumbens is most similar to H. serpyllifolia (both are creepers), but the latter usually exhibits blue flowers (all of which are chasmogamous and above ground; H. procumbens exhibit chasmagamous and cleistogomous flowers, the latter borne underground). Houstonia montana is federally listed as a variety of H. purpurea (Fed E, S2 G2).
No other taxa are listed or proposed for listing, but H. lanceolata (State SR-P, S1 G5) is also of conservation concern and tracked by NHP.
Federally listed taxon—
Houstonia montana (Fed E, State E | S2 G2)
Habitat. Crevices in high elevation rock outcrops or in adjacent balds (ca. 4200 ft
and above).
Range. Endemic to the southern Appalachians of North Carolina and Tennessee.
Additional resources. NHP | Recovery plan | 5-yr review
Key to Houstonia in North Carolina
Key adapted from Radford et al. (1968) and Weakley (2008). Photos by Krings, unless otherwise indicated. Line drawings from Britton & Brown (1913), unless otherwise indicated. Maps courtesy of USDA PLANTS and the North Carolina Natural Heritage Program.
1. Inflorescence appearing very open, diffuse; pedicels 4.5–30x as long as the sepals (usually >6x), flowers terminal (rarely axillary); corolla salverform...2.
2. Stems prostrate, creeping...H. serpyllifolia 
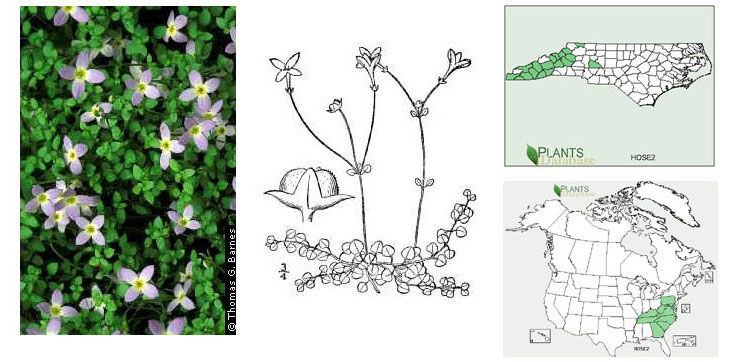

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia serpyllifolia(Photo: Krings)
Houstonia serpyllifolia
(common; cliffs, outcrops, grassy balds, moist forests; Mt)
2'. Stems erect or spreading...3.
3. Plants perennial, basal rosette persistent, well-developed; corolla 5.8–16 (–21) mm long,
tube (2–) 4–11 (–12) mm long, lobes white to light blue, each base with yellow markings...H. caerulea 
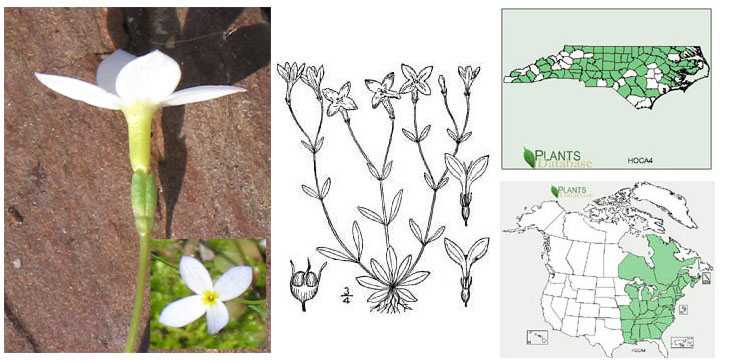

Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Stipule of Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Calyx of Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia caerulea (Photo: Krings)
Houstonia caerulea
(common; disturbed areas, lawns, woodlands, forests; Mt, Pd, CP)
3'. Plants annual, basal leaves few (if any), short-lived; corolla 2–5.5 mm long, tube 0.8–2.8 mm long, lobes lavender, each base with red markings...H. pusilla 
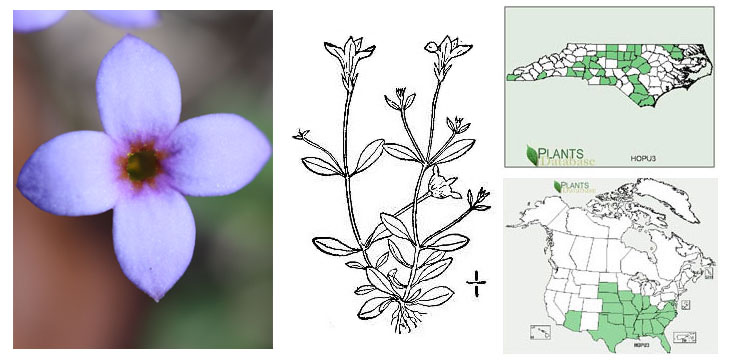

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia pusilla (Photo: Krings)
Houstonia pusilla
(common; disturbed areas, lawns, woodlands; Mt, Pd, CP)
1'. Inflorescence appearing compact, dense; pedicels 1–5x as long as the sepals (usually 1–3x), flowers terminal and axillary; corolla funnelform...4.
4. Leaves ovate or lanceolate (widest toward the base or at the middle),
1–6× as long as wide, 4–34 mm wide; calyx lobes 1–7 mm long...5.
5. Calyx lobes 4–7 mm long; leaves mostly lanceolate (varying from narrowly
lanceolate to broadly ovate), 1.7–3.3 x 0.4–1 cm, 3.3–6× as long as wide...H. lanceolata 
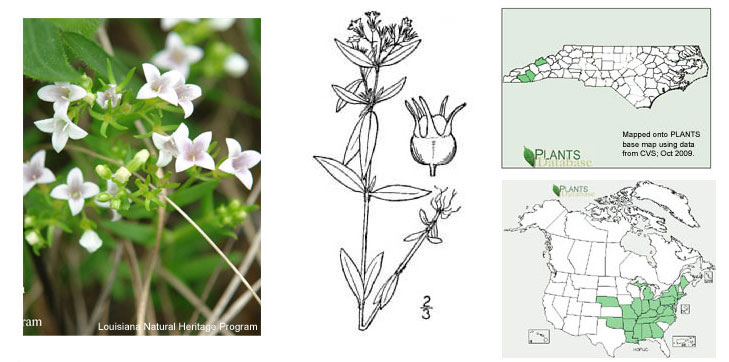

Habit of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Stem and stipule of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Stem and stipule of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Calyx and corolla of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Corolla of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Flowers of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)

Flower of Houstonia lanceolata (Photo: Krings)
Houstonia lanceolata
(rare [State SR-P, S1 G5]; dry banks and woodlands, outcrops, particularly of mafic and calcareous substrate; Mt)
5'. Calyx lobes 1–4 mm long; leaves mostly ovate (varying from broadly ovate to ovate-lanceolate), 0.8–6.3 x 0.6–3.4 cm, 1–3.2× as long as wide...6.
6. Stems glabrous (or slightly shortpubescent on the lower nodes only); adaxial
leaf surface glabrous, blades 3–8 (–13) mm wide; corollas purple, 8–12 mm long; high elevation rocky summits and adjacent grassy balds...H. montana* 
 Houstonia montana*
Houstonia montana*
(rare [Fed E, S2 G2]; crevices of high elevation rock outcrops or gravelly soils
of grassy balds near outcrops; Mt; mid-summer)
6’. Stems sparsely to densely pubescent; adaxial leaf surface sparsely
pubescent, blades (6–) 12–30 (–34) mm wide; corollas light purple to white, (4–) 5–8 (–10) mm long;
habitats various, widely distr...H. purpurea 
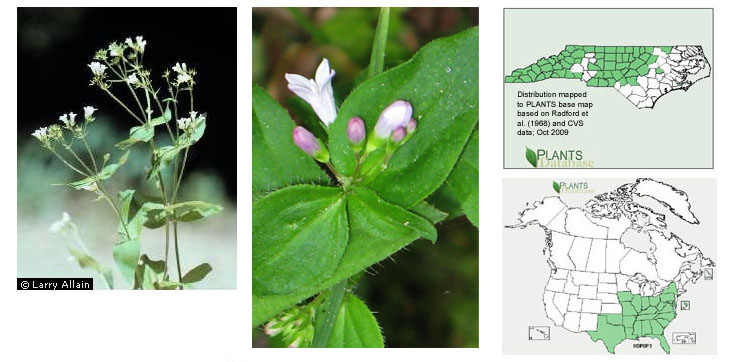

Habit of Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)

Houstonia purpurea (Photo: Krings)
Houstonia purpurea
(common, except rare in CP; moist to dry woodlands and forests, outcrops, disturbed sites; Mt, Pd, CP)
4'. Leaves linear to narrowly elliptic (widest at the middle or toward the apex or nearly equally wide for most of their lengths), 4–20× as long as wide, 0.5–6 mm wide; calyx lobes 0.5–3 mm long...7.
7. Stipules usually broader than long; leaves 1.3–4.7 cm long, 0.5–4.0 mm wide
(mostly < 2.5 mm wide), 7–20× as long as wide; inflorescence very diffuse and open, to 20 cm long, the branches ascending,
spreading, or deflexed, slender and often ultimately filiform, with 1–4 remote nodes bearing reduced leaves,
the pedicels to 14 mm long; internodes mostly 4–9; mature capsules mostly 1.5–2.5 mm long and wide; stem densely cinereous-puberulent, especially at the nodes...H. tenuifolia 
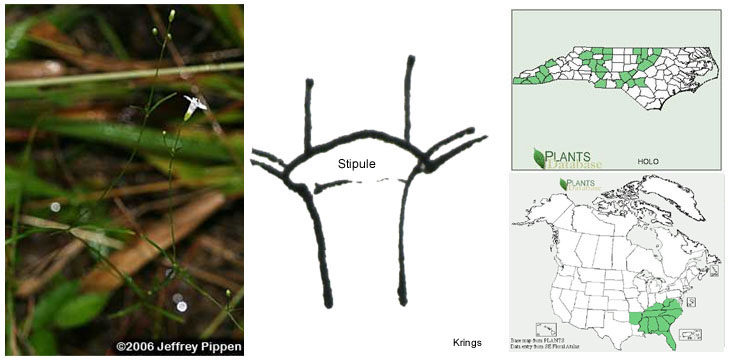

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)

Houstonia tenuifolia(Photo: Krings)
Houstonia tenuifolia
(uncommon, rare in CP; rocky or sandy woodlands, frequently on mafic substrate; Mt, Pd, CP)
7'. Stipules usually longer than broad or as long as broad; leaves 1.6–4.0 cm long, 1.5–6.0 mm wide (mostly > 2.5 mm wide), 4–11× as long as wide; inflorescence rather
open to rather compact, < 12 cm long, the branches ascending or spreading, slender, pedicels to 8 mm long; internodes mostly 7–11; mature capsules mostly 1.8–3.0 mm long and wide; stem densely cinereous-puberulent, glabrate, or glabrous...8.
8. Gap between longitudinal ridges subtending stipules narrow, at least as much stem face visible outside ridges as within; stems glabrous or glabrate
(sometimes puberulent on the nodes only); internodes 7–10, the median internodes (1.1–) 2.0–4.5 (–6.0) cm long; high elevation granitic domes...H. longifolia var. glabra 
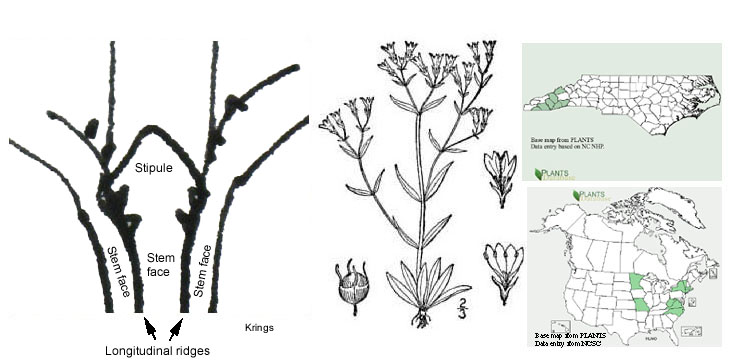 Houstonia longifolia var. glabra
Houstonia longifolia var. glabra
(rare; periodically wet shallow soil mats and crevices of granitic domes; Mt)
8'. Gap between longitudinal ridges subtending stipules broad,
ridges usually at edge of stem face or sometimes a fraction of as much face outside as within visible; stems densely cinereous-puberulent;
internodes (6–) 7–11 (–13), the median internodes (1.0–) 1.5–3.5 (–4.4) cm long; widely distributed...H. longifolia var. compacta 
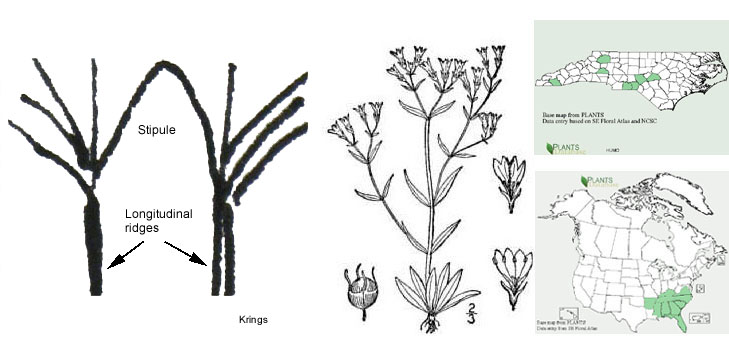 Houstonia longifolia
Houstonia longifolia var.
compacta
(uncommon; dry woodlands, barrens, and road banks, outcrops; Mt, Pd, CP)









