Bark of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)


Bark of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Bark of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Bark of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Bark of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Twig of Acer rubrum (Photo: A. Krings, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)


Twig of Acer rubrum (Photo: A. Krings, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)

Leaves of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)


Leaves of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Leaves of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)
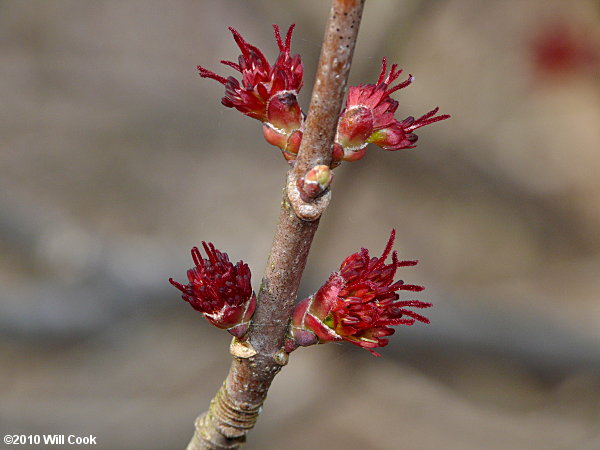

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)


Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Flowers of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)


Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)

Samaras of Acer rubrum (Copyright W. Cook)
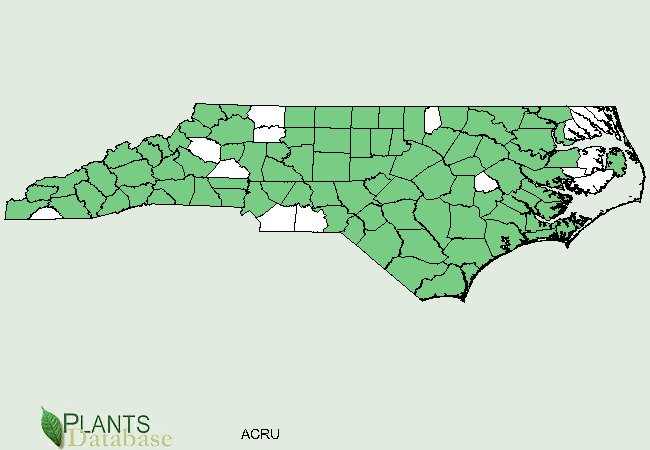
N.C. distribution of Acer rubrum

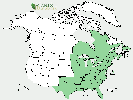
U.S. distribution of Acer rubrum
Acer rubrum (Red maple)
(Common; upland deciduous forests, moist bottomlands and slopes; Mt, Pd, CP; Fl: Jan-Mar, Fr: Apr-Jun)