
(Rorippa palustris (L.) Bess [=R. islandica])
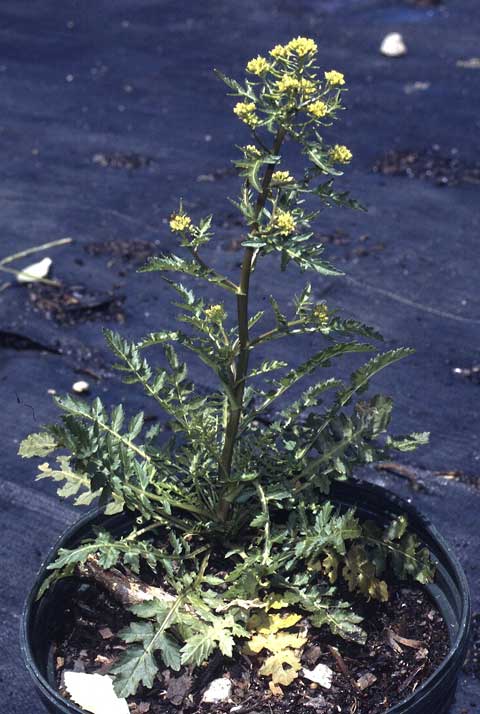

Rorippa palustris habit [Top]

Rorippa palustris stem [Top]

Rorippa palustris abaxial leaf surface [Top]
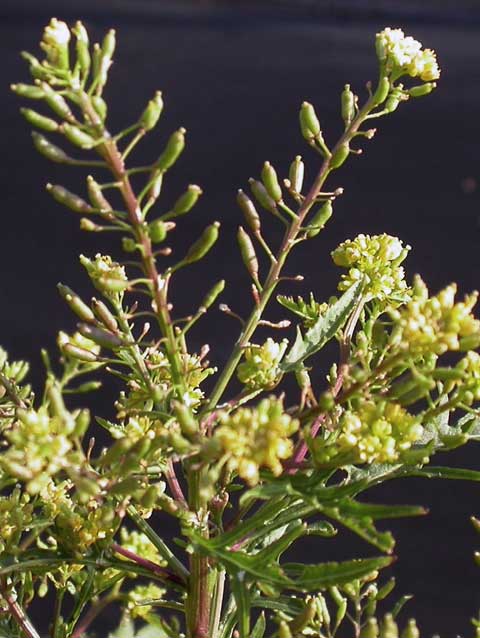

Rorippa palustris fruits [Top]
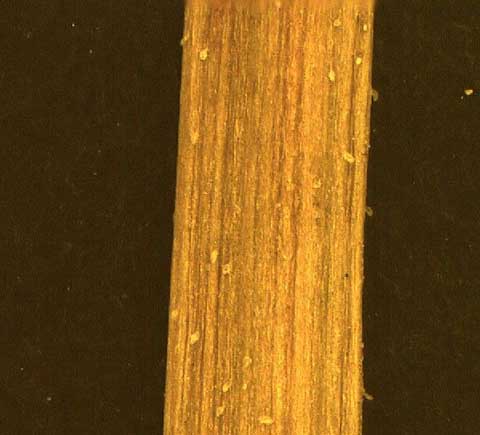

Rorippa teres stem [Top]
Rorippa teres abaxial leaf surface [Top]
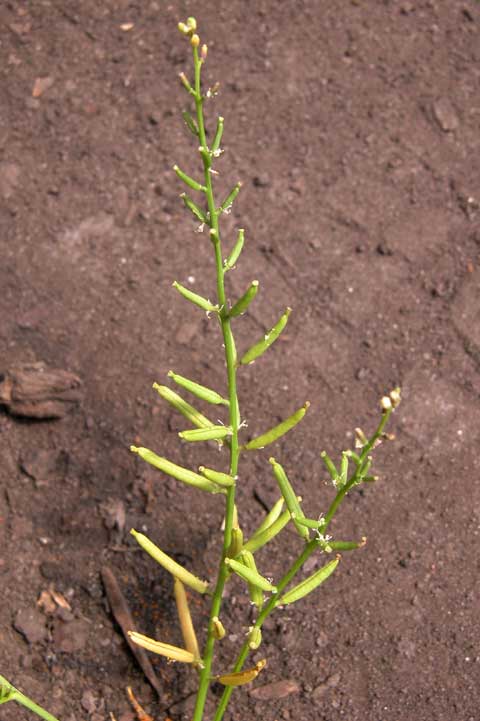

Rorippa teres fruits [Top]
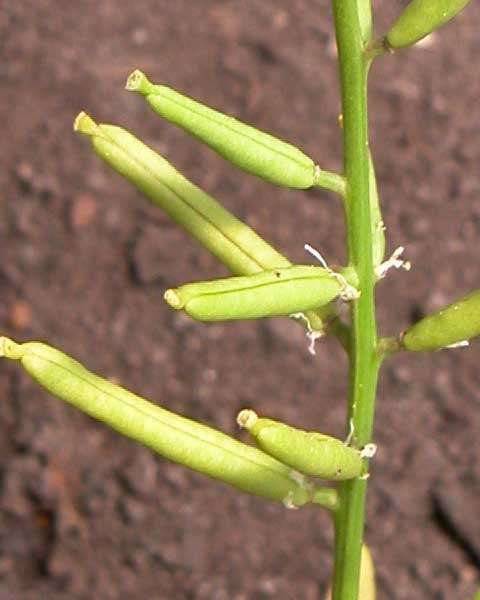

Rorippa teres fruits [Top]
?
G
G
G
?
?
?
?
G
?
G
?
?
Marsh yellowcress and southern yellowcress (Brassicaceae) are very similar winter annual weeds, each widely distributed in the US. These species are most common on moist sites but will grow in many environments. Plants form a rosette with deeply-lobed leaves and erect, branched flower stalks. As plants age, leaves become more deeply lobed. In containers, marsh yellowcress often forms a single erect stem branched only in the inflorescence, but both species may form well-branched mounds. Flowers are yellow and form cylindrical fruit containing many small tan seeds. The species are differentiated by the fruit pods (siliques). Marsh yellowcress seed pods are on short (about � inch) stalks whereas southern yellowcress seed pods lack stalks or are on very short stalks. Both species germinate in fall or spring, in cool moist soils, and are well controlled by several preemergence herbicides. Herbicide efficacy rankings for these species are based on limited experimental data. [TOP]